Definition of Securities:
Financial instruments or certificates that hold value and can be traded are called securities. In addition, “any financial instrument that has a monetary value” is another way to define securities. Financial instruments are cheques, bonds, or securities such as debt and equity. However, it provides quick and easy exchange, buying, selling, and trading between parties and characterizes securities that include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other types of investments. Moreover, investors increase their capital by trading these securities or financial instruments. Furthermore, financial instruments are traded in the open market.
Salient Features:
- These securities or financial instruments can easily be tradeable. Convertible into cash quickly and easily.
- A person or holder who holds financial instruments has the right to get all the benefits related to money under defined sets of conditions.
- They allow you to own the assets without any physical possession.
- The price of these instruments depends on your assets. The higher the price, the higher the value of assets.
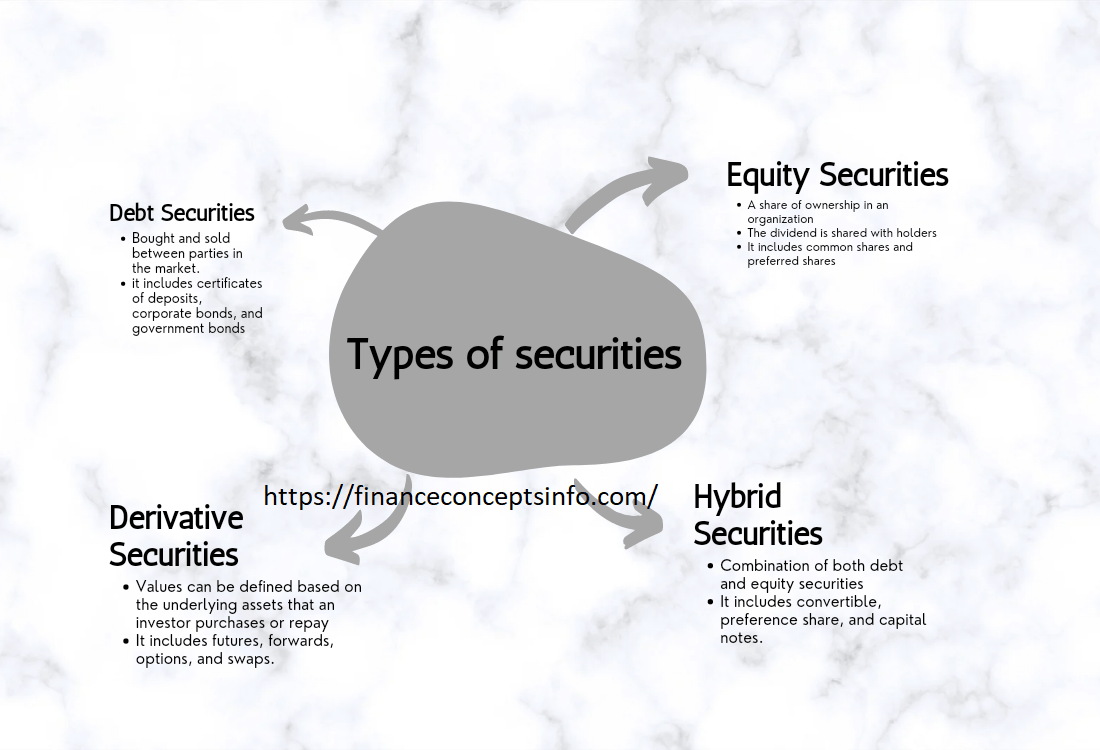
Types of Securities:
Any financial instrument or asset that can be traded on the open market is called a security. There are many types of securities. The main four types are:
- Debt securities
- Equity securities
- Derivatives securities
- Hybrid securities
1. Debt Securities:
In debt securities, governments and corporations raise their capital or funds through publicly traded loans. Regular payments of interest and repayment of the principal loan can be exchanged with these financial instruments, also known as fixed-income securities, which can be traded between parties. However, borrowed funds, interest rate, and maturity date are the major outlines of this debt. In this case, the investor purchases debt securities from the issuer. So the investor is a lender, and the issuer is the borrower. It includes:
Certificates of Deposit (CDs):
A saving account that holds a fixed amount of money for a fixed period is called a certificate of deposit. It may be for six months, one year, or five years.
Government Bond:
A debt security that is issued by the government to support its spending and obligations is called a government bond.
Corporate Bonds:
It is a debt security that is issued by corporations to raise their funds and sold them to their investors.
2. Equity Securities:
A share of ownership in an organization, company, or partnership is called equity security. It can be common stock or preferred stock. Investors become shareholders of the organization by investing in their equity stock. It provides ownership rights to the investors or holders so that they become owners of the firm.
Additionally, the shareholders share the dividend earned through the operational activities of the organization. However, the company’s performance and the financial markets can boost or reduce the value of this security. It Includes;
Common Shares:
It represents the shareholder’s investment in any corporation. In other words, shareholders own corporations. Due to this, investors or shareholders have the right to vote. Additionally, they take part in the decision-making.
Preferred Shares:
In this, the investors or shareholders can claim the earnings of the corporation in the form of dividends and net assets on liquidation. However, preference share can be preferred over common share. The investors have no right of voting.
3. Derivatives Securities:
The securities whose value can be defined, based on underlying assets that an investor can purchase and repay are called derivative securities. However, it is a financial agreement between two parties. Consequently, they buy and sell assets under specific conditions defined by both parties. It is a financial instrument whose values depend on the values of other assets or variables. Similarly, these assets are stocks, bonds, interest rates, and currencies. However, minimization of risk is the main objective of these derivatives. It Includes;
Futures:
Similarly, it is an agreement or contract in which both parties sell and purchase the assets. Both parties agreed on the price at a future date.
Forwards:
Farwords derivatives can be described as customized contract that takes place between 2 different parties or people. They buy or sell their assets at a specified price that can be paid in a future date. Both parties agreed on the terms and conditions stated in the contract. It is risky for both seller and buyer.
Options:
Options are financial derivatives. It is a process in which two parties purchase and sell assets at a predetermined date in the future at a specific price. In this type of contract, the buyers are not required to complete the action of buying and selling.
Swaps:
Two parties exchange financial instruments, known as a swap. In other words, this is a contract in which parties exchange or swap, one kind of cash flow for another. In this agreement, one party fixes a value, while the other party is able to change the other value, which is variable.
4. Hybrid Security
Two or more financial instruments come together to form a security known as a hybrid security. It is a combination of all elements of both debt security and equity security. However, they are complex products. So, they pay high interest at a floating rate at a specific time in the future. They provide a higher rate of return to their investors. These securities protect their investors during bankruptcy. It includes
Convertibles:
It is the security that gives a right to their investors to convert it into another security at a particular date in the future. This type of security provides regular interest to its investors.
Preference Shares:
Preference shares are company stock with dividends paid to their shareholders before the common stock dividends are paid out. They are excellent for risk-averse investors. The issuer can redeem them at any time.
Capital Notes:
A short-term debt instrument or security that the company issues to pay off its short-term obligations is called a capital note. It must be less than the fiscal year. Investors face a high level of risk because these notes are unsecured fixed-income securities.
Markets Where Securities are Traded:
A market is where buyers and sellers exchange goods and services. Financial markets play a vital role in businesses. Trading of securities between two parties or entities occurs in financial markets.
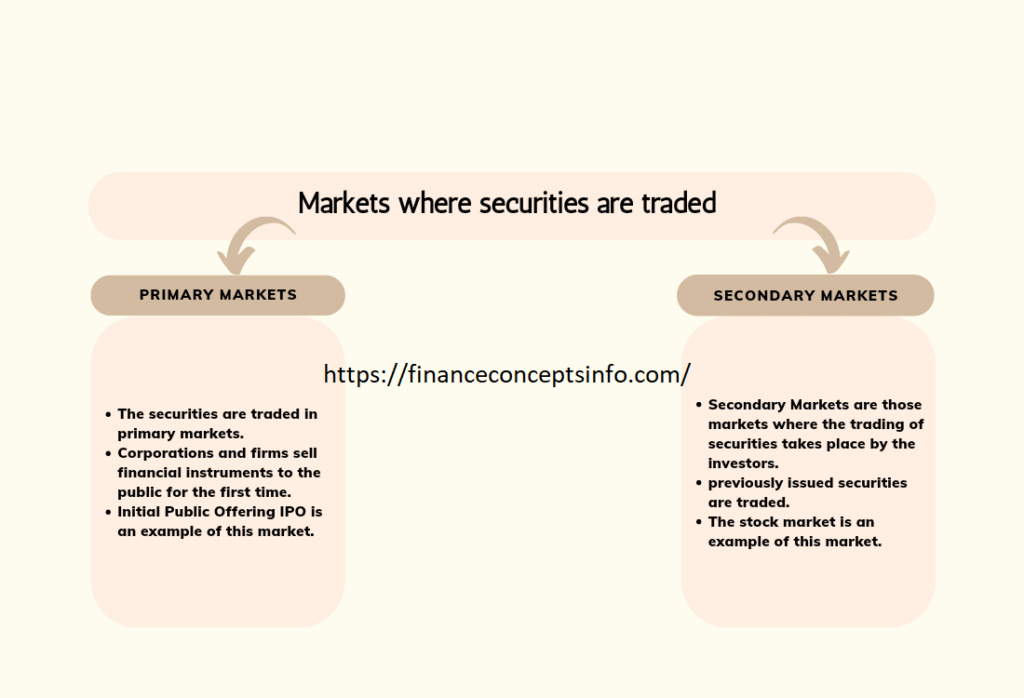
There are two types of markets in which financial instruments can be traded:
- Primary Market
- Secondary Market
1. Primary Market:
Those markets where the securities are created are called primary markets. Nevertheless, for companies or firms that sell financial instruments to the public for the first time, such as new bonds and stocks, the financial instruments are directly purchased from the companies or issuers. The initial public offering (IPO) is an example of this market.
Initial Public Offerings (IPO):
It is a process in which private corporations offer or sell their shares to the public. But it is a new stock that is issued for the first time. Private corporations increase their capital by offering their shares to public investors.
Secondary Market:
Secondary markets are those markets where the trading of securities or financial instruments takes place by the investors. In this market, the investors trade the previously issued financial instruments. The issuing companies cannot be involved in this activity. An example of this market is the stock exchange.
Stock Exchange:
The stock exchange is a place where investors buy and sell existing securities. as it is hosted by the government or any corporation. Ultimately, it includes shares, stocks, bonds, futures, options, etc