Strategic finance implies effectively managing a company’s financial resources. It is done by keeping in mind its short and long-term objectives. This entails analyzing financial data and predicting future trends. Finally, use this knowledge to make carefully considered decisions. Thus, promoting the organization’s financial stability and growth in the long run.
By adopting a strategic mindset toward finances, a company can enhance its financial performance, reduce potential risks and gain maximum profitability. Thus, it is safe to say that strategic finance is the foundation of a company’s financial triumph.
What Is Strategic Finance?
Imagine you’re planning a road trip. You need to know how much money you have and how much you’ll need. Also, where you’ll stop to refuel along the way. That’s what a finance strategic plan does for a business. Moreover, it helps identify the company’s financial situation, its future needs, and the risks it may face.
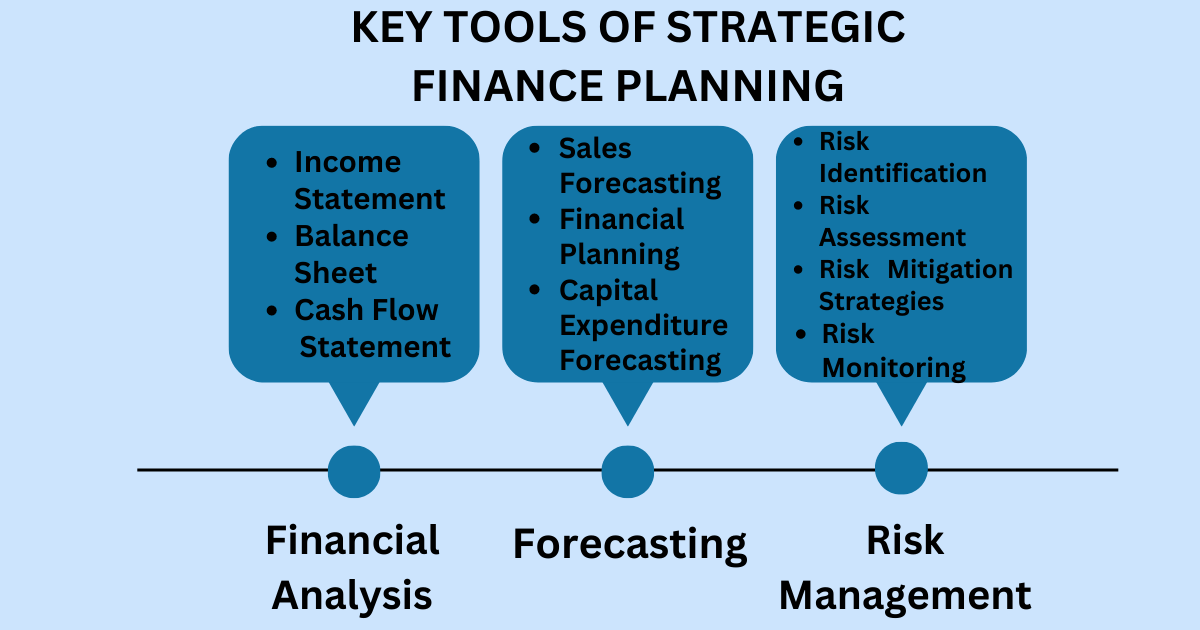
Key Tools Of Strategic Finance Planning:
Let’s have a look at the key tools of strategic finance planning:
Financial Analysis:
It is a process of examining a company’s financial health and current position. It involves looking at various financial statements. This includes income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. All this helps to assess the company’s revenues, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
- The Income Statement
The income statement displays a company’s revenues and expenses for a specific time frame. Financial analysts use it to evaluate if the company is making enough revenue to cover its expenses and generate a profit.
- Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is like a financial snapshot of a company. It shows what a company owns (like money in the bank, inventory, or property) and what it owes (like loans or bills to be paid). It also shows how much money the shareholders have invested in the company.
Strategic planners can use the balance sheet to see the company’s finances’ health. For example, if a company owes more money than it has in assets, it may struggle to pay its debts and need to take action to improve its finances. However, if a company has lots of assets and doesn’t owe much money, it may have more money to invest in things like new products or expand into new markets.
- Cash Flow Analysis
A cash flow statement shows how much money is coming in and going out of a company over a certain period of time. This helps analysts understand how well the company manages its finances. Moreover, this also shows whether it has enough cash to pay its bills and invest in future growth.
For example, if a company is generating a lot of revenue, but its cash flow statement shows that it’s not collecting that money in a timely manner, it may struggle to pay its bills. Conversely, if a company has a lot of cash on hand, it may be in a better position to invest in new projects or expand into new markets.
Forecasting:
- Sales Forecasting:
It is the process of predicting how much a business will sell in the future. To make these predictions, analysts examine past sales data and current market trends. This helps businesses make informed decisions about how much inventory to order and how many employees to hire. Additionally, it also guides them on how much money to spend on advertising.
For instance: A coffee shop can use sales forecasting to decide how much coffee they should buy for the upcoming week. This way, they can avoid running out of coffee, which would cause a problem for their customers. Furthermore, having too much coffee would result in waste and unnecessary expenses.
- Budgeting and Financial Planning:
Budgeting and financial planning involve creating a financial plan for a business’s future activities. This plan includes projections for income and expenses over a set period.
Additionally, budgeting helps businesses manage their cash flow and allocate resources effectively. By setting a budget, a business can avoid overspending. Also, ensure that it has enough money to cover its expenses.
A small business owner might create a budget to plan how much money they will spend on rent, salaries, and supplies over the course of a year.
- Capital Expenditure Forecasting:
Capital expenditure forecasting involves predicting how much money a business will need to invest in capital assets. These include buildings, equipment, and technology. This helps businesses plan for major investments and prioritize their spending.
For example, a construction company might need to invest in new equipment to complete a large project. By forecasting its capital expenditure needs, the company can ensure that it has enough money to make the necessary purchases.
Risk Management:
According to a study by PwC, 60% of CEOs believe that the potential threats to their business have increased in the last few years. This highlights the importance of effective risk management.
- Risk identification:
This involves identifying potential risks, such as financial losses, reputational damage, or legal liabilities. For example, a manufacturer might identify supply chain disruptions or equipment failures as potential risks.
- Risk assessment:
This involves evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks to determine their priority and inform risk management decisions. For example, a financial institution might assess the risk of fraud occurring and prioritize controls to prevent it.
- Risk mitigation strategies:
These are actions taken to minimize or eliminate identified risks. For example, an insurance company might implement fraud detection software to mitigate the risk of fraudulent claims.
- Risk monitoring and control:
This involves ongoing monitoring and control of identified risks to ensure that mitigation strategies are effective and new risks are identified and addressed. For example, a retailer might regularly monitor inventory levels to mitigate the risk of stockouts.