Imagine a world without financial intermediaries. A world where savers and borrowers live in two separate universes. Without any connection. It’s a world where capital allocation is a pipe dream. And economic growth is a faint hope. But thankfully, that’s not the world we live in.
Financial intermediaries act as the matchmakers of the financial system. Thus, bringing together savers and borrowers and allocating capital efficiently. They play a critical role in the economy. Such as enabling smooth transactions and risk transfer flow.
So, let’s unfold the definition of financial intermediaries and explore their importance in the financial system. Buckle up and get ready to be transported into the world of financial matchmakers!
What are Financial Intermediaries?
For instance, you want to buy a new bike. But you don’t have enough money to pay for it upfront. You could go to a bank or credit union. And apply for a loan. If approved, the bank or credit union would lend you the money you need to buy the bike.
Thus, the bank or credit union acts as a financial intermediary by taking in deposits from savers and using that money to make loans to borrowers, like you. In return, the savers earn interest on their deposits. While the borrowers pay interest on their loans.
On one side of the bridge, there are people with extra money who want to invest. However, they may not know the best way to invest it. On the other side of the bridge, there are people who need to borrow money. For instance, they may want to start a business, buy a home, or pay for school.
The financial intermediaries act as the bridge. Thereby, helping those with extra money invest it in a safe and profitable way while also lending that money to those who need it. They provide services like savings accounts, loans, insurance policies, and investment funds to help both sides of the bridge achieve their financial goals.
Types Of Financial Intermediaries:
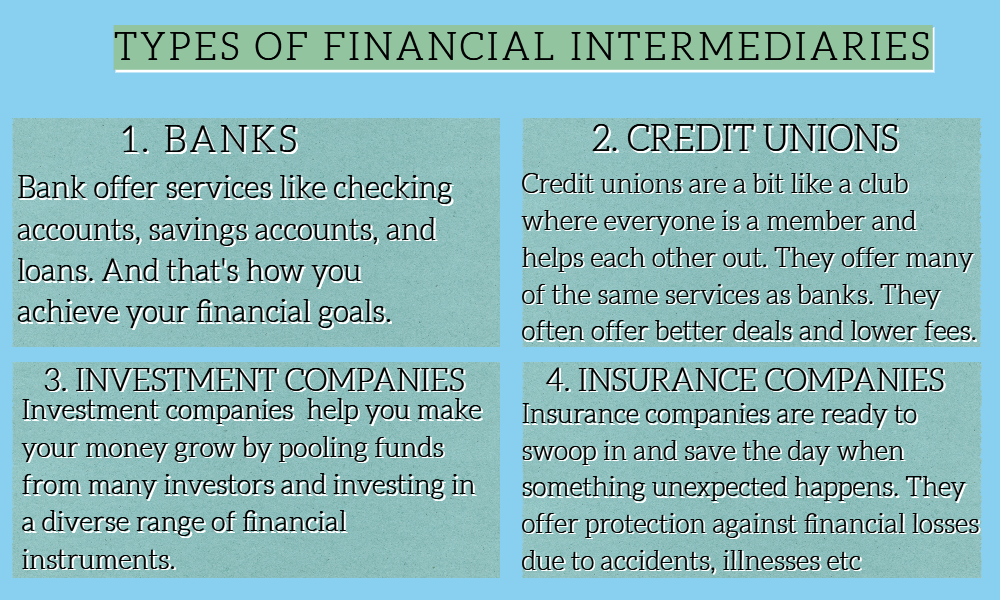
Banks:
Banks are like treasure chests that hold your money. But instead of just keeping it safe, they use it to help other people and businesses grow. They also offer services like checking accounts, savings accounts, and loans. And that’s how you achieve your financial goals.
Did you know that as of 2020, there were over 5,000 commercial banks in the United States with total assets of $22.8 trillion? That’s a whole lot of dough!
Credit unions:
Credit unions are a bit like a club where everyone is a member and helps each other out. They offer many of the same services as banks. But because they are owned by their members, they often offer better deals and lower fees.
As of 2020, there were over 5,200 credit unions in the United States with total assets of $1.7 trillion! That’s a lot of change!
Insurance companies:
Insurance companies are like your own personal superhero. Ready to swoop in and save the day when something unexpected happens. They offer protection against financial losses due to accidents, illnesses, or natural disasters.
Again in 2020, the insurance industry in the United States had a whopping $9.9 trillion in total assets. That’s like having 9,900 stacks of one billion dollars each!
And get this, they generated a staggering $1.3 trillion in premiums! That’s enough money to buy everyone in the world a slice of pizza (or two, if you’re feeling generous).
Investment companies:
Investment companies are like a team of financial wizards. Thus, helping you make your money grow. By pooling funds from many investors, they can invest in a diverse range of financial instruments. This, in turn, helps you achieve better returns on your investments.
In 2020, US mutual fund industry had $22.3 trillion in total assets! That’s like having enough money to buy 111,500 private islands or 223,000 Lamborghinis!
Real-life Examples Of Financial Intermediaries:
1. Robinhood – Empowering the New Generation of Investors:
Robinhood is the go-to platform for those looking to buy and sell stocks. With its intuitive user interface, Robinhood has disrupted the traditional brokerage industry via commission-free trades. In 2021, Robinhood went public with a valuation of $32 billion. All the while, making it one of the most valuable fintech companies in the world.
PayPal – The Pioneer in Digital Payments
PayPal is a household name in the world of digital payments. Founded in 1998, PayPal has revolutionized the way people send and receive money online. In 2021, PayPal processed over $936 billion in total payment volume, with over 377 million active accounts worldwide. PayPal has expanded its offerings beyond online payments. Thus, including peer-to-peer payments, in-store payments, and mobile payments.
Vanguard – Providing Low-Cost Investment Options:
Vanguard offers low-cost investment products to individual and institutional investors. Since its founding in 1975, Vanguard has been a pioneer in index fund investing. Its flagship S&P 500 index fund has some of the lowest expense ratios in the industry. In 2021, Vanguard managed an incredible $8.2 trillion in global assets. This is a testament to the company’s commitment to providing low-cost investment options to its clients.
LendingClub – Connecting Borrowers with Investors:
Since its founding in 2006, LendingClub has helped facilitate over $60 billion in loans! One reason for LendingClub’s popularity is its fixed-rate loans with no prepayment penalties. This makes it an attractive option for those seeking alternatives to traditional lending. Additionally, in 2021, LendingClub made a big announcement. It was acquired by the digital banking company, Radius Bank! This is exciting news particularly, as it shows that LendingClub is continuing to grow and expand its services.
Economies of Scale: A Key Factor in the Existence of Financial Intermediaries:
You might be thinking how do these financial intermediaries profit themselves?
The answer is economies of scale. Basically, it allows the cost per unit of service to decrease as the scale of production or operation increases.
In the case of financial intermediaries, this means that as they gather more funds from investors, they can spread their fixed costs over a larger asset base. Thus, leading to lower costs per unit of service. This enables them to offer a broader range of services at a lower cost than what would be possible for individual investors or small-scale financial firms.
For instance, a significant investment management firm can conduct research and operations for a more extensive portfolio. Thus, reducing the cost per investment. By doing so, they can provide more investment options at a lower cost than small-scale investment firms.
Similarly, a bank can leverage its deposits to make larger loans, reducing the cost of lending per dollar lent. As a result, banks can offer lower interest rates to borrowers than what would be feasible for an individual lender.