What Are The 3 Financial Statements:
The financial statements provide an overview of a company. They tell us important things about a company’s financial position. So, they are essential for handling a company’s funds. They help businesses make good financial choices. We will talk about the main 3 financial statements. We’ll also look at how they affect the growth of a business.
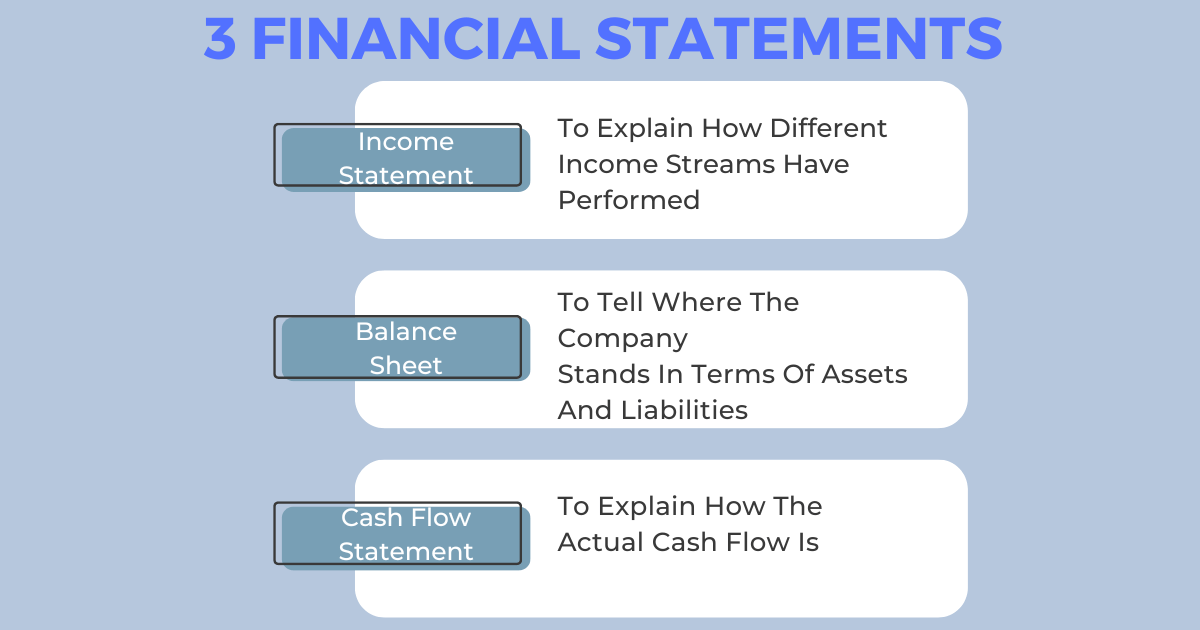
An income statement shows the net income of a period. The balance sheet lists the company’s present assets, debts, and shares. The cash flow statement shows a company’s cash flow over time. This is also necessary to find out its liquidity. Thus, these 3 financial statements help manage a company’s capital.
Investors also count on these three financial statements. They use them to decide whether or not to invest in a company. Managers use them to see how the company is growing. Moreover, these 3 financial statements help the managers make improvements. This helps a company reach its goals easily and quickly.
3 Financial Statements:
These 3 financial statements are income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Let’s take a close look at the 3 important financial statements:
1. Income Statement:
It is the first and most important statement companies use. It is a breakdown of a business’s profits and losses. Therefore, it is also known as an organization’s profit and loss statement.
An income sheet shows a business’s earnings. Profit and loss are the main points of interest. This financial statement also tells about the output of your company. This also includes maintenance costs. Knowing a company’s sales history is useful.
The income sheet has several key parts. So let’s find out what they are:
Revenue:
Revenue is the total amount of profit a company makes. The company makes this money by selling its goods or services. This includes all cash and credit sales.
Cost Of Products Sold:
It involves the charges of making or getting things or services. It covers the cost of labor, supplies, and other expenses. Businesses subtract this cost from income to calculate net profit.
Operating Expenses:
These are the costs of running a business normally. Some of these are rent, salaries, ads, and utilities. Operating income is the company’s regular business income. It’s what’s left after running costs are subtracted from gross profit.
Net income:
It shows the money left over after all bills are taken out. A business also has a net income if it makes more money than it spends. But if its costs are more than its income, it has a net loss.
Earnings Per Share:
You can figure out earnings per share from net income. To find it, divide net income by the number of outstanding shares. Also, a company is more profitable when its earnings per share are higher.
2. Balance sheet:
The balance sheet shows the financial health of a business. It shows what a company owns, what it owes, and how much its shareholders are worth. These three parts make up the value of a business at a certain time.
Also, for the balance sheet to be stable, the assets must match the total of the liabilities and equity. This shows that the balance sheet and records are correct.
The following are the most important parts of the balance sheet; let’s look at them:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholder Equity
Assets:
These are valuable things that a company owns. This includes things like factories, machinery, and shares. Furthermore, intangibles are also a part of it. These are valuable things that you can’t see or touch. Logos, brands, and copyrights are all part of them.
Also, assets are classified by how easily they can be turned into cash. They are divided into current assets or fixed assets. Cash is a short-term asset. It is easy to exchange because of its liquidity. Real estate and machines are long-term assets. They make great fixed assets. This is because it’s difficult to trade them.
Liabilities:
Liabilities are the things and services that a business owes to third parties. This includes borrowing money to start a project, paying workers, and paying taxes. Also, liability is always borrowed and has a monetary value.
The liabilities of a company can be either immediate or long-term. Immediate debts include quick loans, unearned money, and sales taxes that haven’t been paid. Mortgages and bonds are examples of long-term debts.
Shareholder Equity:
Equity is what’s left of a company’s assets after its debts are paid. It covers both common shares and retained profits. Moreover, equity can be either positive or negative. It depends on how much debt the business has compared to its capital.
Debt can be higher than assets, even in companies with greater assets. It means that the shareholder equity is negative.
3. Cash Flow Statement:
The cash flow statement shows how money moves in and out of business. It gives information about a certain time frame. It can be once a quarter or once a year. This statement also gives an overall picture of the company’s liquidity.
It’s a summary of all the cash flows during an accounting period. This includes both incoming and outgoing funds. Period-to-period cash changes are shown in the cash flow statement. So, the cash flow statement may be a better way to show how business liquidity.
The three important parts of the cash flow statement are:
Operating Activities:
The normal cash flow of a business comes from its operational operations. This includes inventory, accounts receivable, and accounts due. Moreover, you can figure out operational cash flow by taking operating actions minus operating expenses.
Investing Activities:
Investing activities are a company’s investments in long-term assets that bring in cash. This includes buying and selling assets and owning shares in other companies. Calculate investment cash flow by subtracting investment cash from investing cash.
Financing Activities:
The cash flows related to a company’s financing are its finance operations. This includes giving dividends to the shareholders. It also means selling bonds or stocks to get cash.
How Are The 3 Financial Statements Linked:
There’s a natural link between these 3 cash statements. The cash flow statement’s operating operations section starts with the net income balance from the income statement. Also, the cash flow statement’s end-of-period amount is shown on the balance sheet. This shows how valuable it is to investors and other parties.
Also, the income statement shows how changes in current liabilities affect income. Cash flows tell us more about the cash assets on a balance sheet. So, they are linked to the net income section of the income statement. So, these 3 financial statements are very important to a business’s growth.